Universal and app links
Overview
Universal links (iOS) and App links (Android) enable an app to respond to specific URLs by navigating to a particular screen or triggering a defined action even if the app is not currently running.
When a user taps a link, the link will decide whether to open the link on the website or in the app.
- If a user is logged into the app, any path whitelisted will navigate to the correct deep linked screen.
- If a user has the app, but is not logged in, then they will be navigated to the login screen.
- If a user does not have the app installed, they will be navigated to the website.
- If the user is on iOS and clicks a universal link from within the VA.gov domain, it will display a smart banner recommending to open the app instead of opening the app directly.
Configurations
If you are adding a new deep link then go adding a new linking path to app section.
iOS
An apple-app-site-association (AASA) file has been uploaded to content-build repository. New paths will require a PR to the content-build repo.
An AASA format will follow a format like this. BundleId and TeamID can be found from the Apple developer account. Additional information about generation of this file can be found here.
{
"applinks": {
"details": [
{
"appIDs": ["<TeamID>.<BundleID>"],
"components": [
{
"/": "/<path>/*",
"comment": "Handles all URLs under /<path>/"
}
]
}
]
},
"webcredentials": {
"apps": ["<TeamID>.<BundleID>"]
}
}
As a more specific example:
{
"applinks": {
"details": [
{
"appIDs": [
"93B5WX72RE.gov.va.vamobileapp",
"W2VK9K4NG2.gov.va.vamobileapp"
],
"components": [
{
"/": "/my-health/appointments/past",
"comment": "Matches any URL with a path that starts with /my-health/appointments/past and send to the mobile app."
},
{
"/": "/my-health/appointments",
"comment": "Matches any URL with a path that starts with /my-health/appointments and send to the mobile app."
}
]
}
]
},
"webcredentials": {
"apps": [
"93B5WX72RE.gov.va.vamobileapp",
"W2VK9K4NG2.gov.va.vamobileapp"
]
}
}
The file uses the following fields to identify associated apps:
appIDs/apps: a unique identifier to distinguish the application. We have two on the va mobile app: one for QA/production and building to device. Another for local development on the emulator. These values can be found on Apple developer account.components: whitelist of acceptable paths the app will navigate to. These paths should mirror the web side while the mobile side consumes them and navigates to the proper screen.
With this in place, the json file should be accessible on the browser. Content should be viewable at:
- https://staging.va.gov/.well-known/apple-app-site-association
- https://www.va.gov/.well-known/apple-app-site-association
Ensure that content-type for this file is application/json when it hits the url
Adding Associated Domain in App Configuration
In XCode, within the “Signing & Capabilities” tab, there should be a section for Associated Domains. Specify the domain of your website with the prefix “applinks.” This informs Xcode that the given domain is intended for Universal Links.

AppDelegate Configuration
Code snippet added in project’s “AppDelegate.mm”
#import <React/RCTLinkingManager.h>
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
openURL:(NSURL *)url
options:(NSDictionary<UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey,id> *)options
{
return [RCTLinkingManager application:application openURL:url options:options];
}
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application continueUserActivity:(nonnull NSUserActivity *)userActivity
restorationHandler:(nonnull void (^)(NSArray<id<UIUserActivityRestoring>> * _Nullable))restorationHandler
{
return [RCTLinkingManager application:application
continueUserActivity:userActivity
restorationHandler:restorationHandler];
Android
An assetlinks.json file has been uploaded to content-build repository. Additional information about generation of this file can be found here
[
{
"relation": ["delegate_permission/common.handle_all_urls"],
"target": {
"namespace": "android_app",
"package_name": "gov.va.mobileapp",
"sha256_cert_fingerprints": [
"04:0F:38:7B:1B:F0:11:D7:4D:2B:C4:B0:EC:AC:9C:A8:95:B9:7C:83:8E:B4:10:CF:EA:6A:C8:E4:E6:86:7A:25",
"FA:C6:17:45:DC:09:03:78:6F:B9:ED:E6:2A:96:2B:39:9F:73:48:F0:BB:6F:89:9B:83:32:66:75:91:03:3B:9C",
"E0:52:25:3C:47:D0:CC:5C:A8:5E:7D:8E:0D:88:8C:1B:A4:CF:87:5E:09:EE:01:C5:A8:C1:12:9F:0B:1E:D3:47"
]
}
}
]
The JSON file uses the following fields to identify associated apps:
package_name: The application ID declared in the app's build.gradle file.sha256_cert_fingerprints: The SHA256 fingerprints of your app's signing certificate- This field supports multiple fingerprints, which can be used to support different versions of your app, such as dev, QA, and production builds
- Fingerprints for production and QA can be found on Google Play Console(App Integrity and Test/Internal app sharing)
- Dev fingerprints are found in Android studio using App Links Assistant or running
./gradlew signingReport
With this in place, the json file should be accessible on the browser. Content should be viewable at:
App settings
After installing the app, you can go to Settings -> Apps -> VA -> Open by default and confirm that staging.va.gov and www.va.gov are verified links
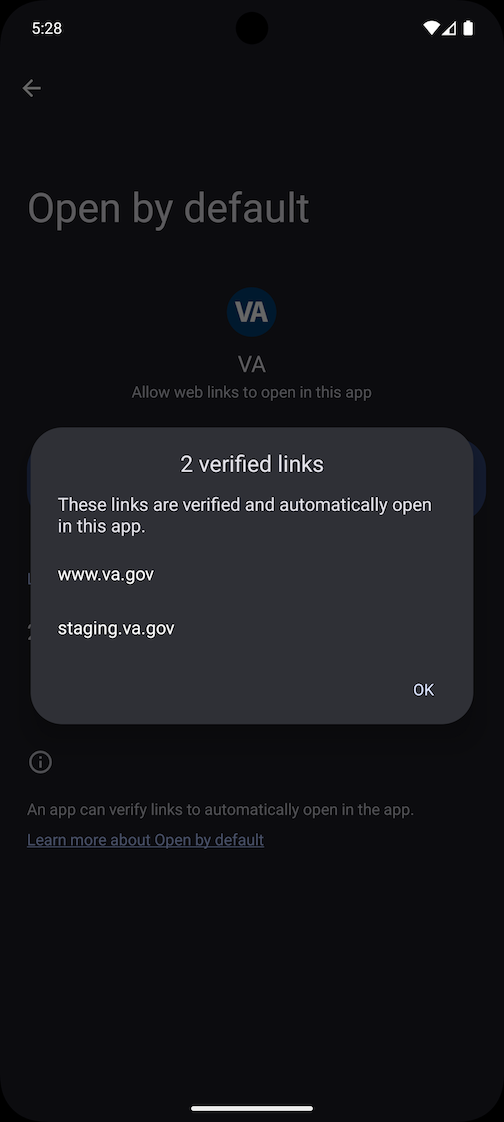
Adding a new linking path in the app
Basic steps
- Obtain the https link that will be used to redirect to the app
ex: https://staging.va.gov/my-health/appointments - Update the
getStateFromPathfunction within thesrc/constants/linking.tsxfile. An example is provided below.
- Note that within the
prefixesarray,https://staging.va.govandhttps://www.va.govhave already been added. If your new universal link does not include these options as a prefix, a new element will need to be added here in addition to the relevant portions within the configurations.
// Handles https://staging.va.gov/my-health/appointments & https://staging.va.gov/my-health/appointments/past
if (pathParts[0] === 'my-health' && pathParts[1] === 'appointments') {
const isPastAppointment = pathParts[2] === 'past'
return {
routes: [
{
name: 'Tabs',
state: {
routes: [
{
name: 'HealthTab',
state: {
routes: [
{ name: 'Health' },
{ name: 'Appointments', params: isPastAppointment ? { tab: 1 } : { tab: 0 } },
],
},
},
],
},
},
],
}
}
- Updates will now need to be made for both iOS and Android
Android
-
Update the Android manifest file. On Android studio navigate to
Tools->App Links Assistant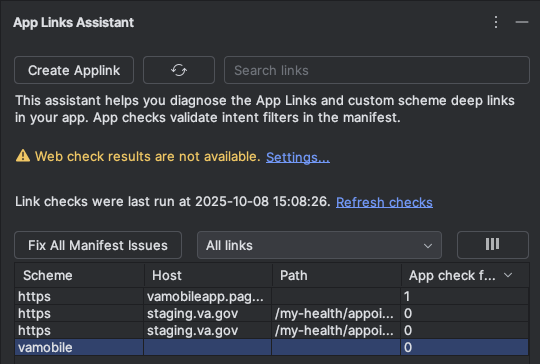
-
Click on
Create Applink->Open URL Mapping Editor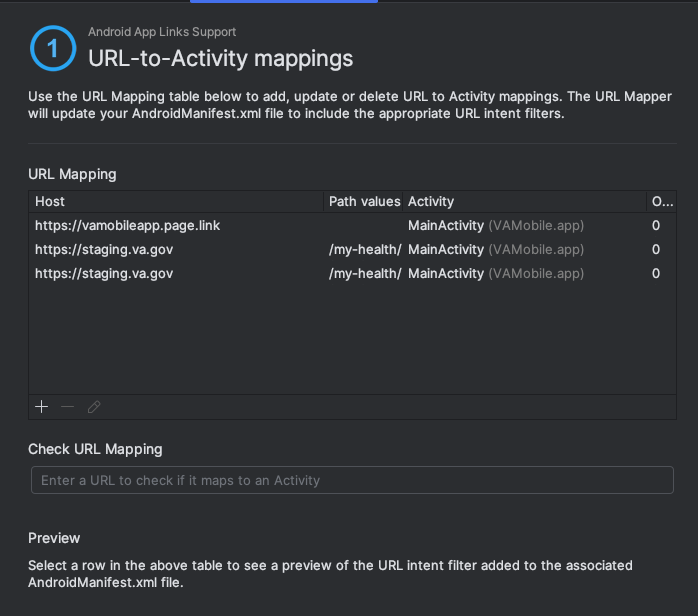
-
Click on the
+button and add the new path. This should automatically update the Android Manifest file.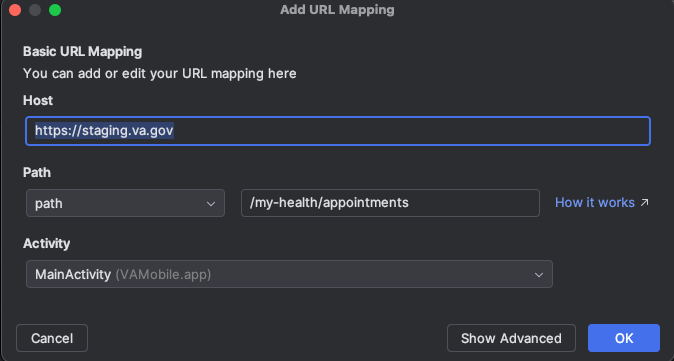
-
The android manifest file should add a snippet similar to the following
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="staging.va.gov" />
<data android:path="/my-health/appointments" />
</intent-filter>
Ensure that android:autoVerify="true" is present.
Add a path for both staging.va.gov and www.va.gov as QA builds and local testing are done using staging to verify and va.gov for production.
iOS
- Updates will need to be made to the apple-app-site-association file by adding a new object representing the new universal link within the
componentsarray. This requires a PR to be made to thecontent-buildrepository. More information about preparing a PR
Make sure to validate that the result is valid json after the update
"components": [
{
"/": "/my-health/appointments/past",
"comment": "Matches any URL with a path that starts with /my-health/appointments/past and send to the mobile app."
},
{
"/": "/my-health/appointments",
"comment": "Matches any URL with a path that starts with /my-health/appointments/ and send to the mobile app."
}
]
Testing
Before testing deep links, make sure that you rebuild and install the app in your emulator/simulator/device. Testing can be done on the emulator or on a physical device for both iOS and Android.
Log into demo mode or a user before deep linking, or you will land on the initial screen of the app instead of the intended screen.
For iOS, deep links can be tested on staging.va.gov and www.va.gov domains once updates to AASA file have been updated and can be viewed via public url.
On Android, staging.va.gov and www.va.gov can be used once the AndroidManifest updates have been made as the assetLinks.json does not require additional changes usually.
Opening deep links
On devices, you can use the following to test your deep links:
- opening a link from an email
- tapping a link on slack
- text message or notifications
Android
Android has an additional way to test deep links.
Command line
The adb command can be used to test deep links with the Android emulator or a connected device:
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d [your deep link]
As an example:
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "https://staging.va.gov/my-health/appointments"
Useful Links
https://medium.com/@fashad.ahmed20/how-to-implement-universal-links-in-react-native-19a424db4dcf
https://reactnavigation.org/docs/deep-linking/
https://developer.android.com/training/app-links/about
https://www.ebay.com/.well-known/apple-app-site-association
https://www.ebay.com/.well-known/assetlinks.json
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/xcode/supporting-associated-domains